The idea of the metaverse has sprung from science fiction and is becoming a reality due to the quick development of technology and the changing nature of digital culture. We shall examine the history, present status, and potential future consequences of the metaverse in this comprehensive review.
What is the Metaverse?
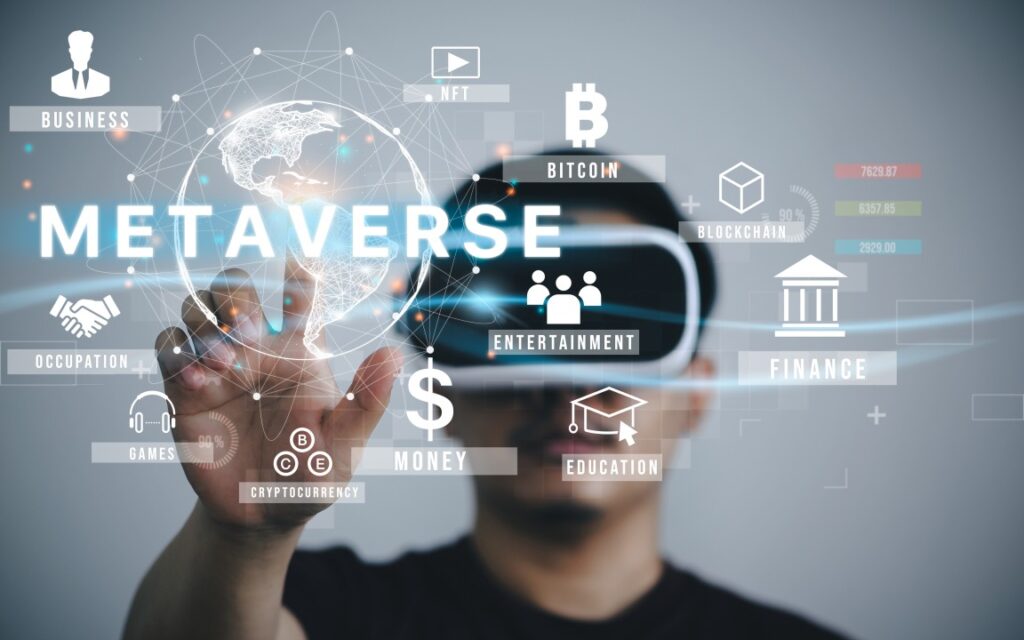
Fundamentally, the term “metaverse” describes a shared collective virtual environment that is produced by the merging of physically persistent virtual reality with virtually augmented physical reality. Users can participate in a variety of activities in this realistic and interactive virtual world, including intricate simulations and social interactions. Since its initial use in Neal Stephenson’s science fiction book Snow Crash in 1992, the term has expanded to include a wide range of virtual experiences made possible by state-of-the-art technologies.
Early Virtual Worlds
In the late 1970s and early 1980s, early virtual worlds like MUDs (Multi-User Dungeon) marked the beginning of the path toward the present metaverse. These text-based settings served as a precursor to more complex graphical virtual worlds. More graphical and interactive virtual places were made available in the 1990s by websites like Second Life and Habbo Hotel, which let users construct and communicate in three-dimensional (3D) environments. These platforms illustrated how virtual environments may support both social and commercial activity.
Technological Advancements
The development of important technologies gave rise to the metaverse concept:
simulated Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR transports users into completely simulated worlds, whilst AR superimposes digital data on the real world. The development of captivating metaverse experiences requires the use of both technologies.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies: In virtual worlds, blockchain technology allows for safe transactions and decentralized control. NFTs (non-fungible tokens) and cryptocurrencies enable economic transactions and digital ownership in the metaverse.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): By enabling intelligent virtual agents and customizing user experiences, AI improves the metaverse. Algorithms powered by AI are capable of producing dynamic material, handling intricate interactions, and producing lifelike avatars.
5G and Edge Computing: These developments offer the low latency and bandwidth required for real-time interactions in the metaverse. 5G networks are currently being deployed.
Major Players
Meta (previously Facebook): With its Horizon Workrooms virtual collaboration platform and Oculus VR headsets, Meta is making significant investments in the metaverse. The company envisions a fully integrated digital economy and social ecology within the metaverse.
Microsoft: One aspect of Microsoft’s metaverse strategy is the integration of its Mesh technology with Microsoft Teams to offer mixed reality collaboration tools. The business is also looking into enterprise and gaming applications for the metaverse.
Epic Games: A significant force in the metaverse, Epic Games is the company behind Fortnite. Numerous virtual environments are powered by the Unreal Engine, and the business is creating technologies to enable user-generated content and virtual experiences.
Roblox: Roblox is a platform that allows users to create their own games and experiences, geared at younger users. Users can now make, purchase, and sell virtual goods and experiences in a thriving virtual economy.
Emerging Trends
Interoperability: The capacity of various virtual environments to communicate with one another is essential to the metaverse’s future. The development of standards and protocols that enable smooth movement and communication across multiple platforms is now under progress.
Digital Identity and Personalization: People will look for more individualized metaverse experiences, where their digital avatars represent their actual identities and preferences. Improved DIT management will be essential to a seamless user experience.
Virtual Economies: Through virtual goods, services, and currencies, the metaverse is promoting new business prospects. Online events, virtual fashion, and digital real estate are quickly growing into important sources of income for businesses and creators alike.

Privacy and Security
As the metaverse develops, security and privacy issues become more important. Concerns of user permission and data privacy are brought up by the gathering and handling of enormous volumes of personal data in virtual worlds. Strong cybersecurity defenses are necessary to prevent fraud and security breaches.
Digital Divide
There is a chance that the metaverse will widen the already existent digital divide. In order to engage with the metaverse, one must have access to high-speed internet, sophisticated gadgets, and computer literacy. To guarantee inclusion and equitable opportunity for all users, these gaps must be filled.
Ethical and Regulatory Issues
New moral and legal dilemmas brought about by the metaverse include those involving digital ownership, intellectual property rights, and content moderation. To solve these issues and guarantee a just and responsible metaverse, it will be crucial to create precise rules and laws.
The Future of the Metaverse
The metaverse is still in its early phases, and continued study and advancement will determine how it develops in the future. We may anticipate the metaverse becoming more immersive, participatory, and ingrained in everyday life as technology develops.
Potential Scenarios
Work and Education: By offering immersive virtual settings for collaboration and learning, the metaverse has the potential to completely transform remote work and education. Virtual offices and courses might proliferate, presenting fresh opportunities for interaction and connection.
Entertainment and Social Interaction: Virtual concerts, events, and social places will probably become a regular part of our lives as the metaverse’s role in entertainment grows. Users might come across novel storytelling and interaction formats.
Economic Integration: New business prospects and models may result from the integration of the real and virtual economies. Online services, digital goods, and virtual real estate will all become more and more important to the world economy.








Leave a Reply